Introduction
Many Muslims around the world are excited for Ramadan, the holiest month in Islam. As it gets closer, people often ask, “How many days are left for Ramadan?” Knowing the exact date helps in preparing for fasting, prayers, and other activities.
This guide will answer all your questions about Ramadan 2025, including the expected start date, the Ramadan calendar 2025, and tips on how to prepare for this special month.
Ramadan Calender 2025
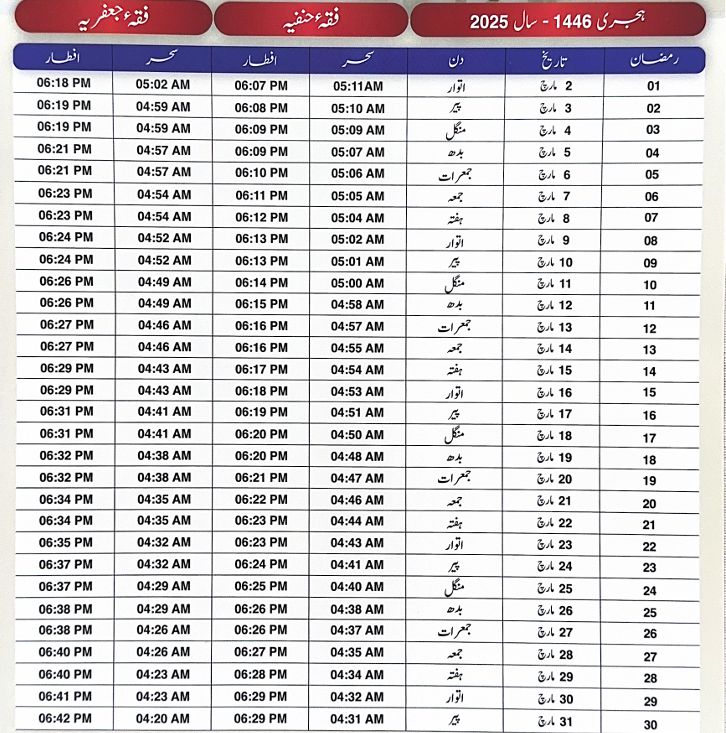
How Many Days Until Ramadan 2025?
Ramadan follows the Islamic lunar calendar, which means it starts with the sighting of the new moon. Based on predictions, Ramadan 2025 will begin on the evening of March 1, 2025, and last until March 31, 2025. However, the exact date may change depending on the moon sighting in different countries.
Ramadan 2025 Calendar – Important Dates
A Ramadan calendar helps Muslims manage their fasting and prayer times. Here are the important dates for Ramadan 2025:
- Start Date: Evening of March 1, 2025
- First Fast: March 2, 2025
- Mid-Ramadan (15th Day): March 16, 2025
- Last Fast: March 31, 2025
- Eid-ul-Fitr: April 1, 2025
Why Is Ramadan Important?
Ramadan is not just about fasting. It is a time to connect with Allah, purify the heart, and help those in need. Here’s why Ramadan is special:
- Fasting (Sawm): Muslims do not eat or drink from sunrise to sunset to learn patience and self-control.
- Prayers: Muslims offer extra prayers, including Taraweeh, at night.
- Charity (Zakat & Sadaqah): Giving money and food to the poor is encouraged.
- Quran Reading: Many people try to read or finish the Quran during Ramadan.
How to Prepare for Ramadan 2025?
To fully enjoy and benefit from Ramadan, proper preparation is important. Here’s how you can get ready:
- Change Your Routine: Start waking up early for Suhoor (pre-dawn meal) and reduce late-night activities.
- Plan Healthy Meals: Eat balanced Suhoor and Iftar meals to stay strong and active.
- Increase Worship: Start praying more and reading the Quran before Ramadan begins.
- Give Charity: Set aside money for Zakat and Sadaqah to help the needy.
- Set Goals: Decide how much prayer, Quran reading, and charity you want to do during Ramadan.
Ramadan Mubarak – A Special Greeting
As Ramadan approaches, Muslims say “Ramadan Mubarak” to wish each other a blessed month. This greeting is shared in person, over the phone, and on social media to spread joy and positivity.
Conclusion
Now that you know how many days are left for Ramadan 2025, it’s time to start preparing for this blessed month. Follow a plan, increase your worship, and take part in charity.
Ramadan Mubarak to all! May this Ramadan bring peace, happiness, and blessings to you and your family.
FAQs About Ramadan 2025
Q1. When does Ramadan 2025 start?
Ans: Ramadan 2025 is expected to start on the evening of March 1, 2025, with the first fast on March 2, 2025.
Q2. How long will Ramadan last?
Ans: Ramadan will last for 29 or 30 days, ending on the evening of March 30 or 31, 2025.
Q3. Why is Ramadan important?
Ans: Ramadan is a time for fasting, prayer, charity, and self-improvement for Muslims worldwide.
Q4. How is the date of Ramadan decided?
Ans: Ramadan starts with the sighting of the new moon according to the Islamic calendar.
Q5. What are the best foods for Suhoor and Iftar?
Ans: For Suhoor, eat oats, eggs, yogurt, and fruits to stay full longer. For Iftar, start with dates and water, followed by light meals like soup, rice, and grilled food.
Q6. When is Eid-ul-Fitr 2025?
Ans: Eid-ul-Fitr will be celebrated on March 31 or April 1, 2025, marking the end of Ramadan.
Q7. Is fasting required for everyone?
Ans: Fasting is compulsory for all adult Muslims, except those who are sick, pregnant, traveling, nursing, or menstruating.